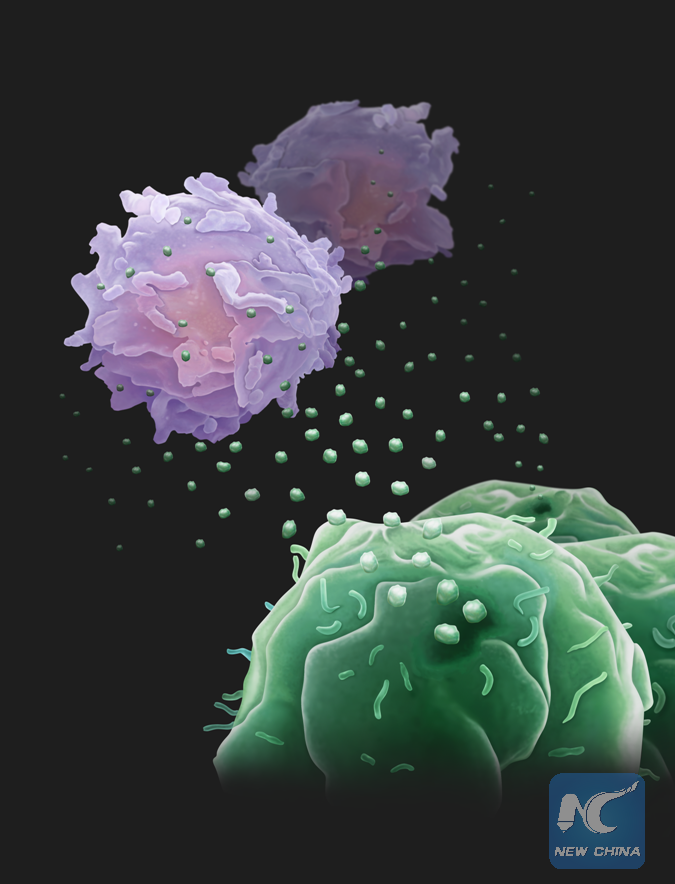
Secretion of exosomes by tumor cells (lower right) to fight the T cells (upper left). (Xinhua/Credit: The labs of Wei Guo, PhD, and Xiaowei Xu, MD, PhD, University of Pennsylvania)
WASHINGTON, Aug. 8 (Xinhua) -- American and Chinese researchers found cancer cells could send out biological "drones" to fight the immune system for their own control.
A study published on Wednesday in the journal Nature showed that cancer cells could release small vesicles called exosomes circulating in the blood and armed with proteins called PD-L1, causing T cells to tire before they have a chance to reach the tumor.
The research signals a paradigm-shifting in which cancers can take a systemic approach to suppressing the immune system and points to a new way to predict which cancer patients will respond to anti-PD1 therapy that disrupts immune suppression to fight tumors.
Anti-PD1 therapy blocks interaction between PD-1, a protein on the surface of T cells, and PD-L1, the PD-1's counterpart molecule on tumor cells, thus reinvigorating T cells and allowing them to unleash killing power on the tumor.
"Immunotherapies are life-saving for many patients with metastatic melanoma, but about 70 percent of these patients don't respond," said Guo Wei, a professor of Biology at the University of Pennsylvania.
In this new work, the team found that exosomes from human melanoma cells carried PD-L1 on their surface, including those of breast and lung cancers. Those exosomes can directly bind to and inhibit T cell functions.
"Identification of a biomarker in the bloodstream could potentially help make early predictions about which patients will respond," said Guo.
According to the paper's co-author Xu Xiaowei, a professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at the university, exosomes are tiny lipid-encapsulated vesicles with a diameter less than 1/100 of a red blood cell.
Since a single tumor cell is able to secrete many copies of exosomes, the interaction between the PD-L1 exosomes and T cells provides a systemic and highly effective means to suppress anti-tumor immunity in the whole body, according to the study.
But the exosomes in the bloodstream presented a way of monitoring the cancer-versus-T cell battle via a blood test, helping measure the effectiveness of a treatment.
"In the future, I think we will begin to think about cancers as a chronic disease, like diabetes," said Guo.
"Just as diabetes patients use glucometers to measure their sugar levels, it's possible that monitoring PD-L1 and other biomarkers on the circulating exosomes could be a way for clinicians and cancer patients to keep tabs on the treatments," said Guo.
Researchers from Wuhan University, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Wistar Institute, University of Texas and Mayo Clinic collaborated in the study.

